Missions
Select a Mission for full overview.
In Development

FURST
FURST (Full-Sun Ultraviolet Rocket Spectrometer) is a sounding rocket mission that will attain the first high-resolution, radiometrically-calibrated spectrum of the Sun's vacuum ultraviolet rays.

IMPRESS
The IMPRESS mission (Impulsive Phase Rapid Energetic Solar Spectrometer) is a 3U CubeSat designed to investigate particle acceleration in solar flares.

MUSE (ASIO)
The ASIO (formerly BUBO) instrument is the successor to CAPRI-SUN. Instead of being launched on a sounding rocket, it will be a payload on the MUSE satellite being built by Lockheed Martin.
Ongoing

REAL
The overarching objective for the REAL (Relativistic Electron Atmospheric Loss) CubeSat is to improve our understanding of the physical mechanisms responsible for scattering radiation belt electrons into the atmosphere.

SFXTI (EISSFLAIX)
The SFXTI instrument (also known internally as EISSFLAIX) is a derivation of the IMPRESS instrument that is intended to collect data from solar radiation on the exterior of the ISS.

Ground Station (K7MSU)
SSEL's ground station, callsign K7MSU, was setup to track SSEL satellites, as well as other ameature-band satellites.
Completed

RadPC-Lunar
The RadPC payload is an experiment for testing the reliability of a radiation tolerant computer system when exposed to solar radiation on the Moon's surface.

BOOMS
BOOMS is a high-altitude balloon mission that is intended to observe flashes of X-rays in the polar atmosphere known as microbursts.
Hi-C Flare (CAPRI-SUN)
The CAPRI-SUN instrument is intended to capture soft X-ray time series from solar flares at an unprecedented 1-kHz cadence. CAPRI-SUN will be part of the Hi-C (High-resolution Coronal Imager) Flare sounding rocket mission.

IT-SPINS
The Ionospheric-Thermospheric Scanning Photometer for Ion-Neutral Studies (IT-SPINS) mission proposes to provide the first two-dimensional (2D) tomographic imaging from a 3U research CubeSat, addressing the basic nature of the nocturnal ionosphere.

FIREBIRD II
The FIREBIRD II mission (Focused Investigations of Relativistic Electron Burst Intensity, Range, and Dynamics) was a targeted, goal-directed, space weather CubeSat mission to resolve the spatial scale size and energy dependence of electron microbursts in the Van Allen radiation belts.

FIREBIRD
The FIREBIRD mission sought to accomplish the same goals as its successor FIREBIRD II, which was to resolve the spatial scale size and energy dependence of electron microbursts in the Van Allen radiation belts.

HRBE - EP1
The Hiscock Radiation Belt Explorer (HRBE), named in honor of Dr. William A. Hiscock, founder of the Montana Space Grant Consortium, launched from Vandenberg Airforce Base in California on October 28, 2011.

EDSN
The Edison Demonstration of Smallsat Networks (EDSN) mission sought to demonstrate the use of inter-satellite communications across a swarm of eight small satellites to collect and relay multipoint, scientific measurements from a loose formation orbiting about 500 km above Earth.

IRIS
The primary goal of the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph (IRIS) explorer was to understand how the solar atmosphere is energized. The IRIS investigation combined advanced numerical modeling with a high resolution UV imaging spectrograph.

MOSES & ESIS
Our next-generation imaging spectrographs, MOSES (Multi-Order Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrograph) and ESIS (Extreme Ultraviolet Snapshot Imaging Spectrograph), obtained spectroscopic data over a wide field of view in every exposure. We were able to get comprehensive observational access to the physics of reconnection events, for the first time observing reconnection “from the inside out.”
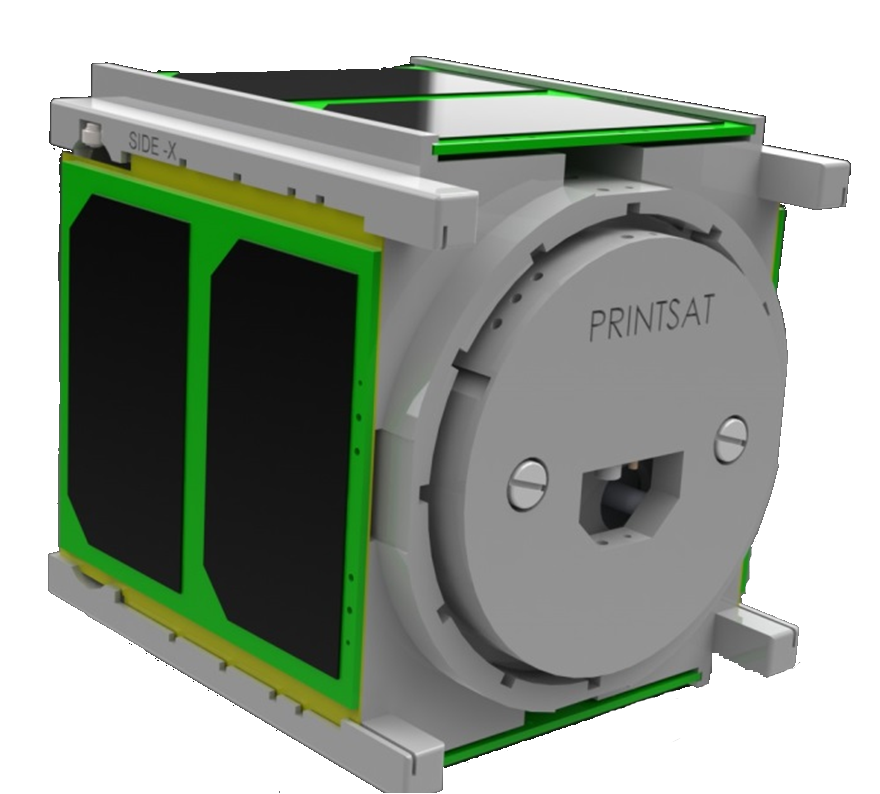
PrintSat
The PrintSat mission was a technology demonstration to access the effectiveness of additive manufacturing (i.e. 3D printing) and the Windform XT material for use as a material for space structures.
